- e-mail us
- We are Open
Study in USA
- Home
- Study in USA

Studying in the United States is a significant interest for Kurds. American universities attract numerous international students due to their exceptionally high educational standards. Kurds also seek to move to the United States through education,
Topics covered in this article:
– Requirements of studying in US
– Can children be admitted to US schools?
– Steps for undergraduate admissions
– Steps for postgraduate admissions
– Applying for PhD program in US
– Educational scholarships
– Costs of studying & living in US
– Working while studying in US
– Criteria for dependent visa
– Top Universities in US
– Necessary Documents for student visa
– Finding a job after graduation in US
– Gain US citizenship via education
– Commonly Asked Questions
– Last words about Studying in US

Requirements of studying in US
When discussing immigration through education in the United States, it’s important to provide some foundational context about the country. If you’re already familiar with the United States, feel free to skip this section and proceed to the information on studying there.
The United States, located in North America, is a federal republic made up of 50 states, one federal district, five territories, and various islands. It is one of the most diverse nations in terms of race and nationality. Covering an area of 9.8 million square kilometers, the U.S. has a population of approximately 325 million people, making it the fourth largest and third most populous country globally. The capital is Washington, D.C., while New York City is the most populous city. The country shares borders with Canada to the north, Mexico to the south, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. The official currency is the dollar, and English is the primary language.
The United States boasts one of the world’s top education systems, with prestigious colleges and universities that consistently rank highly on global lists. Degrees from American institutions—whether bachelor’s, master’s, or PhDs—are widely recognized and respected around the globe. This reputation attracts many international students, but it’s important to approach the application process with caution.
Can children be admitted to US schools?
Immigrating to the United States through education is not a straightforward process. Elementary education in the U.S. consists of five years, covering grades 1 through 5. Overall, students typically spend six years in school, including kindergarten. The academic year begins in September, and students can attend either public or private schools. In the United States, education includes six years of elementary school, three years of middle school, and four years of high school. Private schools tend to be quite expensive but offer high-quality education and facilities. In contrast, public schools are free and provide a more standard level of education. Approximately 85 to 90 percent of American students attend public schools. International students generally do not have the opportunity to enroll in American schools unless they are living in the U.S. with their parents, who must have obtained U.S. citizenship. In such cases, children can attend schools in the United States.
Steps for undergraduate admissions
Immigrating to the United States for a bachelor’s degree can be an objective for many applicants. Students typically enter universities after completing 12 years of schooling. Therefore, international students aspiring to enroll in U.S. universities for a bachelor’s program must possess a high school diploma. Students have the option to pursue a 1- or 2-year course leading to an Associate Degree (if they hold an 11-year diploma) or a 4-year program for a bachelor’s degree (with a 12-year diploma). After enrollment, students must declare a major by their second year of college.
One crucial requirement for admission at this stage is achieving an IELTS score of 6 or an equivalent TOEFL score. If the average score is below 16, it may be advisable to first complete a 2-year Associate Degree before transitioning to the bachelor’s level. Students can study various disciplines, including management, law, engineering, science, biology, and education.
To gain admission to U.S. universities for a bachelor’s degree, students must take an exam outlined below:
SAT REASONING TEST: This assessment is mandatory for undergraduate admission to U.S. universities.
SAT SUBJECT TEST: This exam evaluates students’ knowledge and skills in specific subjects.
SAT TEST: This test assesses four areas: English, mathematics, reading, and science, and includes an optional writing component. The score indicates students’ preparedness for college entry.
Steps for postgraduate admissions
Applicants seeking to immigrate to the United States for a master’s degree can take the necessary steps. To qualify for this level, students must have completed 16 years of formal education, which includes 12 years of schooling and a 4-year bachelor’s degree. A master’s degree in the United States typically takes 2 years to complete. Students can gain admission to various fields of study, but they must take the following exams to be eligible for the master’s program:
TOEFL
This test evaluates students’ proficiency in four language skills: speaking, listening, writing, and reading. A minimum score equivalent to an IELTS 6 is required.
GRE
Those wishing to pursue a master’s degree in the United States must take this examination and achieve a passing score. Administered by the ETS (Educational Testing Service), it assesses verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, critical thinking, and analytical writing skills.
GMAT
This test serves as the admission exam for management programs and is a standardized assessment for MBA candidates. Initially designed for business and management courses at U.S. universities, it is now utilized by over 1,700 institutions worldwide.
LSAT
This examination is required for law school admissions. It is a standardized test necessary for entry into LSAC-accredited law schools and is offered four times a year.
MCAT
Commonly known as the Medical College Admission Test, this exam is administered by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and is a critical component of the medical school admission process.
Applying for PhD program in US
Another pathway for immigration to the United States through education is pursuing a PhD. A crucial factor is that the applicant must present a strong research proposal and demonstrate a high level of language proficiency, typically requiring an IELTS score of 7 or higher. Additionally, having a supervisor is vital during the PhD process. A PhD program in the United States generally spans 4 to 6 years.
Here are some key points to consider:
The PhD phase in the United States is primarily research-oriented and holds significant prestige. Earning a PhD requires 3 to 6 years of dedicated study. U.S. universities are categorized into two main types: public and private institutions. Public universities tend to be more affordable, but there may be restrictions on admitting international students.
Based on whether they serve as research centers, U.S. universities can be classified into two groups:
GROUP ONE
Universities that function as both educational institutions and research centers, actively accepting PhD candidates.
GROUP TWO
Universities that are not research institutions, focusing solely on education, offering programs that typically last 2 to 4 years. The highest degree these universities provide is the bachelor’s degree.
Most U.S. institutions welcome students and offer the majority of scholarships during the fall semester (September and October). International students aiming to study and immigrate to the United States through education must undertake certain examinations and achieve satisfactory scores.
Educational scholarships
Many applicants seeking to immigrate to the United States through education are interested in scholarships. However, obtaining a scholarship, particularly for a PhD, necessitates meeting specific criteria, such as a high language proficiency score, outstanding academic performance, a strong GPA, an impressive research proposal, published ISI articles, recommendation letters, and securing a supervisor. The United States offers scholarships at various educational levels.
For undergraduate programs, students must present high scores in their high school diploma and TOEFL or IELTS language assessments, and they should not have significant gaps in their education. In such cases, students can apply for scholarships after receiving admission.
At the master’s and PhD levels, students are required to submit the GMAT for management courses, GRE scores for engineering programs with a minimum score of 70, and LSAT for law programs. Currently, obtaining scholarships is quite challenging, and only students who meet these criteria may have a chance of receiving one.
Costs of studying & living in US
The cost of studying in the United States varies by university. Tuition at private institutions can reach around $60,000, making it quite expensive. Students seeking more affordable options can consider state or public universities, where the cost for American residents is approximately $9,139, while international students face different rates. Tuition for international students ranges from $15,000 to $22,000 for a bachelor’s degree, $18,000 to $25,000 for master’s programs, $18,000 to $25,000 for PhD programs, and $35,000 to $50,000 for medical sciences.
we will discuss living expenses in United States, which are very high compare to Kurdistan.
States and cities of the United States | Yearly expenses of life in USD |
Boston (Massachusetts), Miami (Florida) | About 20,000 to 25,000 |
Atlanta | About 18,000 to 20,000 |
Philadelphia | 20,000 to 22,000 |
Washington D.C and New York | 22,000 to 30,000 |
Los Angeles (California) | 22,000 to 30,000 |
San Francisco | 20,000 to 26,000 |
Seattle (Washington) | 23,000 to 26,000 |
Chicago | 16,000 to 22,000 |
Ohio | 18,000 to 23,000 |
Detroit (Michigan) | 19,000 to 22,000 |
Dallas (Texas) | 20,000 to 24,000 |
Working while studying in US
One common concern for students immigrating to the United States is the ability to work while studying. In the U.S., students are permitted to work both on and off campus. For on-campus jobs, no work permit is required; however, students must obtain a work permit from the Immigration Office to work off-campus. Similar to regulations in other countries, students may work up to 20 hours per week during their undergraduate studies and up to 30 hours per week for master’s and PhD programs. Students can utilize job search websites to find employment. It’s important to note that obtaining a student visa for the United States is not an easy process and can be quite complicated.
Criteria for dependent visa
When it comes to immigration through study in the United States, acquiring a dependent visa is a key concern for students. Those with a student visa can apply for a dependent visa for their spouse and children under 21 years of age. However, obtaining a dependent visa for children over 21 may take longer, potentially exceeding six months. Additionally, permanent residents may face longer processing times for dependent visas compared to U.S. citizens, who can typically obtain these visas more quickly.
Another crucial factor in securing a dependent visa is that if dependents have serious or incurable illnesses or a criminal record, their visa application may be denied. Demonstrating financial capability to cover living expenses in the U.S. and proving that there is no need for government assistance can significantly enhance the chances of obtaining a dependent visa.
Top Universities in US
In the context of immigration through study, it is important to recognize that the United States is home to many highly ranked universities, attracting numerous applicants and talented individuals. Graduating from top universities in the U.S. often leads to high-paying job opportunities and access to lucrative job markets. There are both public and private institutions in the U.S. that rank among the best in the world. Below is a table showcasing some of these prestigious universities. This content is provided by Talav Company, and all rights are reserved. Unauthorized copying without permission, documentation, or citation is prohibited.
|
Name of university |
Information |
|
Harvard University |
This university was founded in 1636 in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Harvard is the first private university in the US. It’s also among top 10 universities in the world. |
|
Stanford University |
Founded in San Francisco, California. It’s among top 10 universities of the world and is the 3rd wealthiest. |
|
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
Founded in Cambridge, Massachusetts in 1861. Has many colleges and majors. |
|
Columbia University |
Located in New York, New York. Accepts students in medical sciences, art, law, and engineering. It’s the 5th oldest university in the US. |
|
University of Berkeley (California) |
Located in Berkeley, California. Built in 1868. Offers many scholarships |
|
University of Chicago |
Located in Chicago, Illinois. Built in 1890. |
|
Princeton University |
Located in Princeton, New Jersey. Built in 1746. At first it was a college and after creating various faculties, it was converted into a university. |
|
Cornell University |
Located in Ithaca, New York. Built in 1865. Accepts students in various courses. |
Necessary Documents for student visa
When seeking to study in the United States, specific documents are necessary based on the type of student visa. Below is a breakdown of the main student visas and the required documentation:
F1 Visa
The F1 visa is the most common visa for international students enrolling in colleges and universities. Spouses and dependent children under 21 can apply for the F2 visa. This visa is typically for courses lasting longer than six months. For application, students must complete the DS-160 form after receiving the I-20 form from their institution.
M1 Visa
The M1 visa is designed for students pursuing vocational or technical studies. Similar to the F1 visa, applicants can bring their spouse and children under 21 with an M2 visa. The DS-160 form must also be completed for this visa.
J1 Visa
The J1 visa is intended for those involved in research or teaching at universities. The duration of the J1 visa depends on the course length, but applicants are generally required to return to their home country for two years before reapplying for entry. The J2 visa is available for spouses and children under 21. Like other visas, the DS-160 form is required.
For all the above visas, applicants must demonstrate financial capability and intent to return to their home country after completing their studies. Although U.S. institutions offer English courses for students without language proficiency, obtaining a language certificate is crucial for visa approval.
Key Documents Required for a Student Visa
- English CV
- Recommendation Letters: At least three for Master’s and four for PhD programs.
- Statement of Purpose (SOP)
- Confirmation Letter: From university officials or the International Student Office for Master’s and PhD degrees.
- Research Proposal: For graduate studies.
- Proof of Financial Capability
- Admission Letters: From the university and professors for Master’s and PhD applicants.
- Criminal Record Clearance and Health Certificate
- Lease Agreement and Insurance Letter
Finding a job after graduation in US
Typically, the ability to secure a job is influenced by the skills and qualifications of the student. It is essential for students to be proficient in English and demonstrate their capabilities to potential employers. It’s important to note that employers often prefer to hire U.S. citizens over non-citizens. However, individuals who have graduated from American universities generally have a greater chance of finding employment compared to those who entered the country primarily for work.
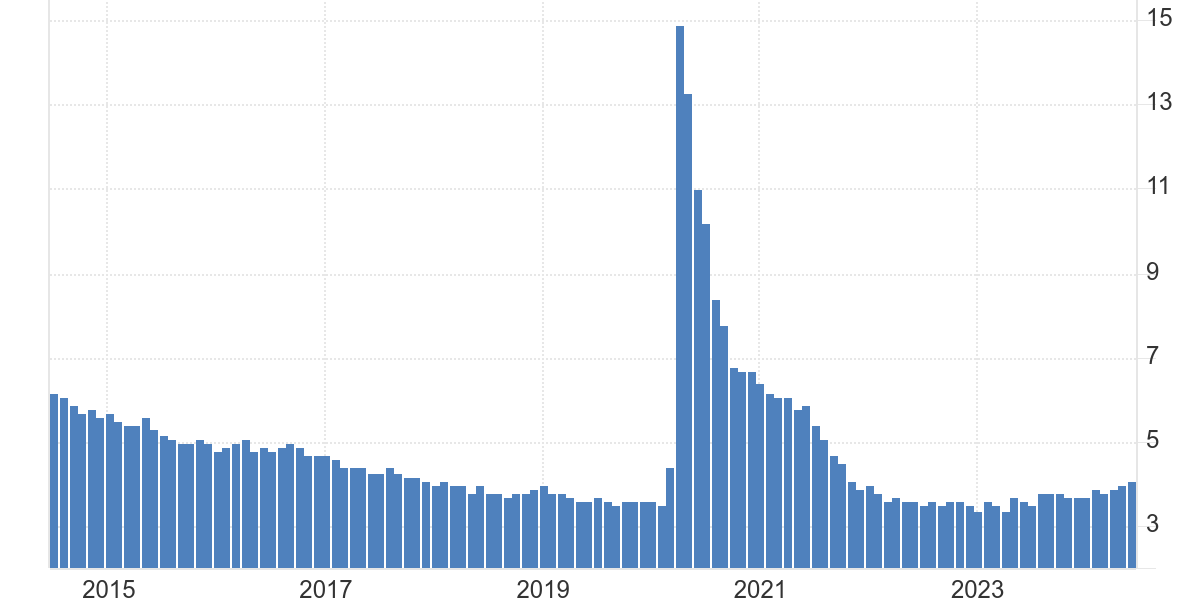
Graduates can search for job opportunities directly or utilize websites and recruitment agencies to find their ideal positions quickly. Generally, students must leave the United States within 60 days of graduation unless they manage to transition their student visa to a work visa. This means graduates have a 60-day window to secure employment after completing their studies. unemployment rate in the United States decreased from 2015 & 2023.
Gain US citizenship via education
People who enter the United States usually intend to acquire residency and citizenship after graduation. For this purpose, these people must find a job in the United States after graduation, or investing, or marry an American citizen. Among these options, finding a job is the best because investing requires a lot of investment. People who succeed in finding a job, can acquire permanent residency and American Green Card after paying tax regularly for a few years. After that they can take action to acquire citizenship and passport of this country but keep in mind that finding a job for non-Americans can be hard. The length of time to get to permanent residency of the United States is different and depends on the type of their temporary residency. People who have acquired permanent residency can get passport and citizenship after 5 years.
Commonly Asked Questions
✅ Is studying in the United States free?
No, you must pay tuition fees unless you receive scholarships.
✅ Can you study in the U.S. without a language qualification?
Yes, but to improve your chances of obtaining a visa, it’s advisable to have a language qualification.
✅ Is it possible to get scholarships from U.S. universities?
Scholarships are typically awarded to PhD students, and you will need an impressive CV, including a high language score and published articles in reputable journals.
✅ Can you work in U.S. after graduation?
After graduation, you have the opportunity to seek employment in the U.S. If you are successful, you can change your status from a student visa to a work visa.
Last words about Studying in US
topic of immigration through study to the U.S. and its various conditions has been addressed from a scholarly perspective. It’s important to note that currently, pursuing immigration to the U.S. through education presents its own challenges and difficulties. Therefore, individuals considering this path may also want to explore opportunities in countries such as Canada, Austria, Denmark, the Netherlands, Switzerland, or Finland before attempting to immigrate to the U.S. for study. For further assistance, you can always reach out to our expert colleagues at Talav Company for free consultation via phone regarding immigration to leading countries. Feel free to leave your questions in the comments section, and you will receive a prompt response.

for immigration & Travel
Useful Links
Warning! The information provided on this website is based on research conducted by non-legal professionals, and Talav Company does not assume legal responsibility for the accuracy or reliability of this content.
We highly recommend that you independently verify this information and consult with a qualified local attorney to ensure it is applicable to your specific situation.